Russia puts Ukrainian President Zelensky on its wanted list
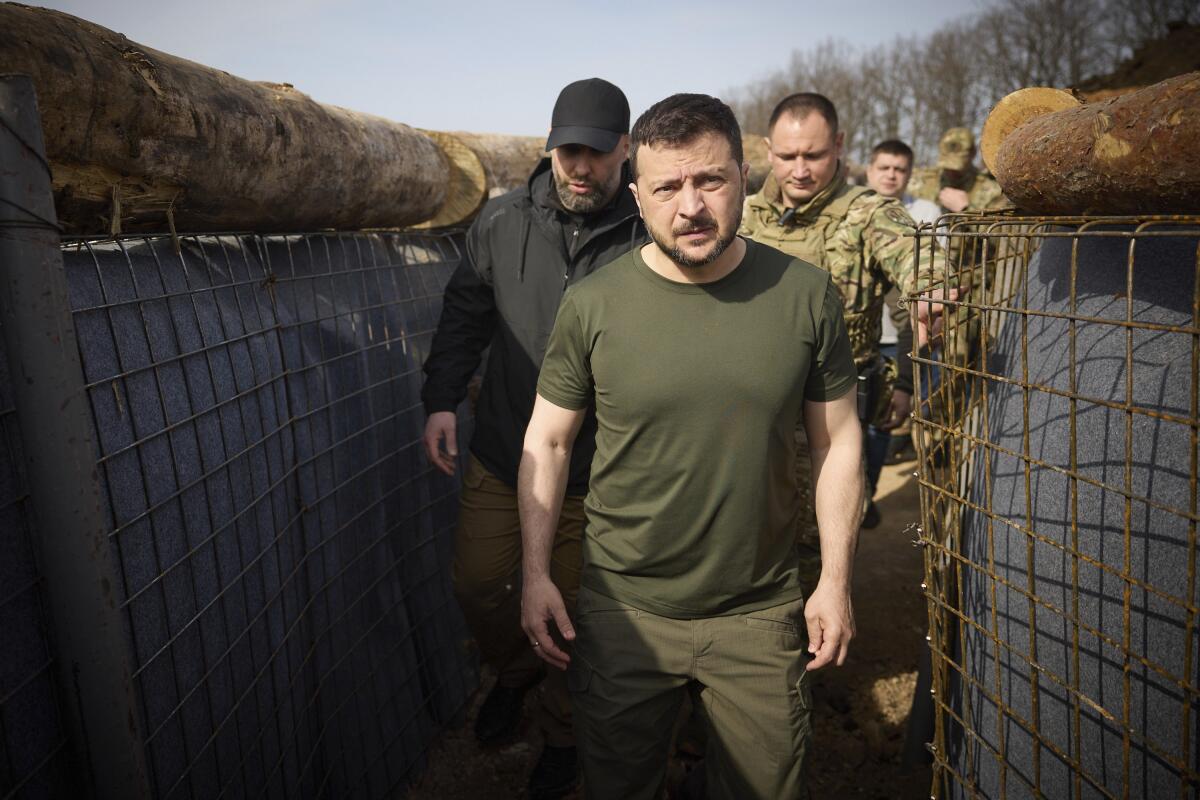

Russia has put Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky on its wanted list, Russian state media reported, citing the interior ministry’s database.
Zelensky and his predecessor, Petro Poroshenko, were on the ministry’s list of people wanted on unspecified criminal charges. Gen. Oleksandr Pavlyuk, who is commanding Ukraine’s ground forces in the war against Russia’s invasion, was also on the list.
Russian officials did not immediately clarify the allegations. Mediazona, an independent Russian news outlet, claimed Saturday that both Zelensky and Poroshenko had been listed since at least late February.
Ukraine’s foreign ministry dismissed the reports of Zelensky’s inclusion as evidence of “the desperation of the Russian state machine and propaganda.”
Kharkiv, Ukraine’s second-largest city, is facing intense Russian airstrikes, but its residents are defiant. “We can stand up, no matter what they do,” one said.
Russia’s wanted list includes scores of officials from Ukraine and North Atlantic Treaty Organization countries. Among them is Kaja Kallas, the prime minister of NATO and European Union member Estonia, who has fiercely advocated for increased military aid to Kyiv and stronger sanctions against Moscow.
Russian officials have said Kallas is wanted over efforts to remove Soviet-era monuments to Red Army soldiers in the Baltic nation. Fellow NATO members Latvia, Lithuania and Poland have also pulled down monuments widely seen as an unwanted legacy of the Soviet occupation of those countries.
Russia has laws criminalizing the “rehabilitation of Nazism” that include punishing the “desecration” of war memorials.
Also on Russia’s list are cabinet ministers from Estonia and Lithuania, as well as the International Criminal Court (ICC) prosecutor who last year prepared a warrant for President Vladimir Putin on war crimes charges. Moscow has also charged the head of Ukraine’s military intelligence, Kyrylo Budanov, with what it deems “terrorist” activities, including Ukrainian drone strikes on Russian infrastructure.
Could Ukraine lose the war? Once nearly taboo, the question hovers in Kyiv, but Ukrainians believe they must fight for their lives against Putin’s troops.
Amid worsening Ukraine war outlook, an infusion of American military aid is seen as crucial in the fight against Russian invaders. Will it be enough?
The Kremlin has repeatedly sought to link Ukraine’s leaders to Nazism, even though the country has a democratically elected Jewish president who lost relatives in the Holocaust, and despite the aim of many Ukrainians to strengthen the country’s democracy, reduce corruption and move closer to the West.
Moscow named “de-Nazification, de-militarization and a neutral status” of Ukraine as the key goals of what it insists on calling a “special military operation” against its southern neighbor. The claim of “de-Nazification” refers to Russia’s false assertions that Ukraine’s government is heavily influenced by radical nationalist and neo-Nazi groups — an allegation derided by Kyiv and its Western allies.
The Holocaust, World War II and Nazism have been important tools for Putin in his bid to legitimize Russia’s war in Ukraine. World War II, in which the Soviet Union lost an estimated 27 million people, is a linchpin of Russia’s national identity, and officials bristle at any questioning of the USSR’s role.
Some historians say this has been coupled with an attempt by Russia to retool certain historical truths from the war. They say Russia has tried to magnify the Soviet role in defeating the Nazis while playing down any collaboration by Soviet citizens in the persecution of Jews, along with allegations of crimes by Red Army soldiers against civilians in Eastern Europe.
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.