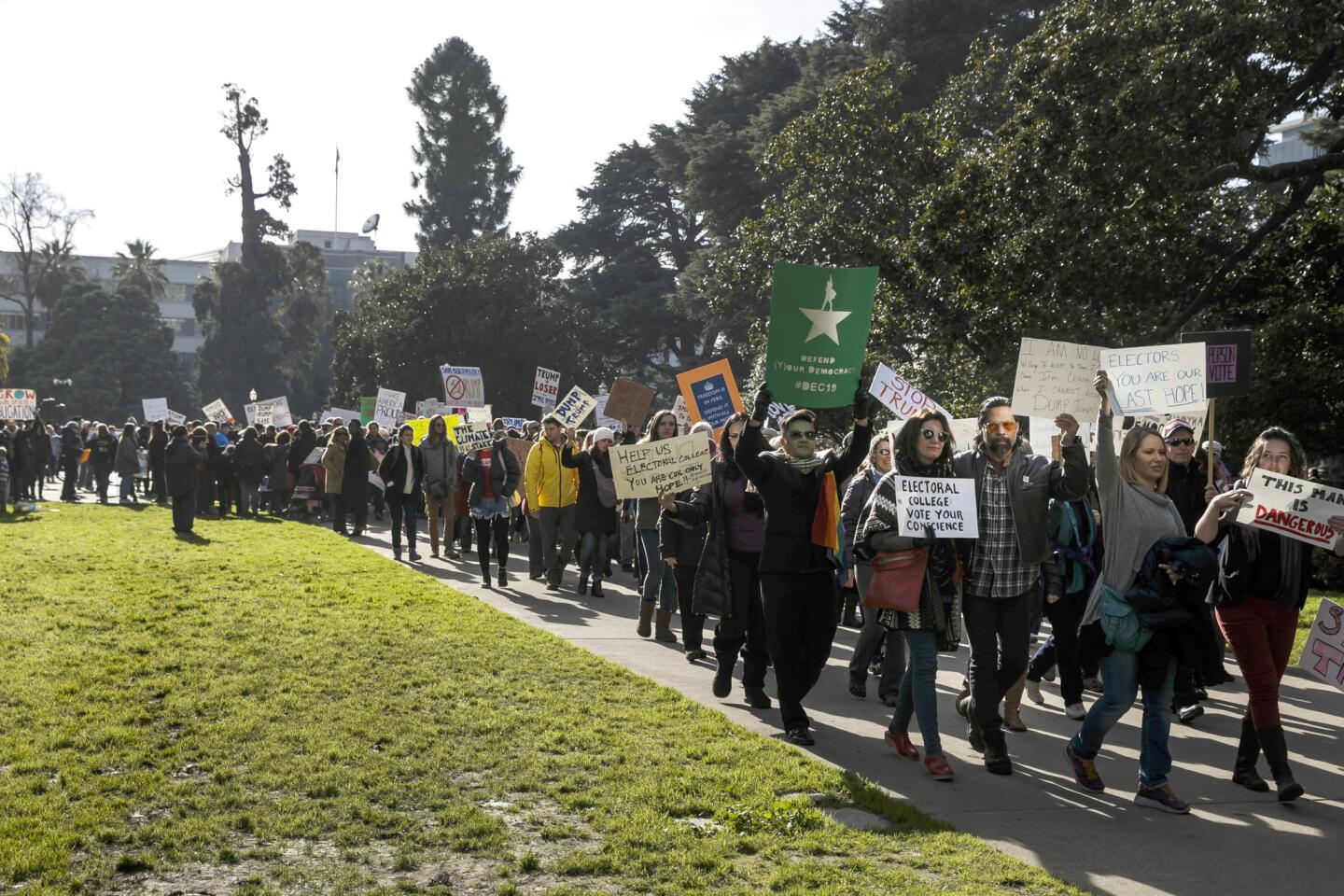
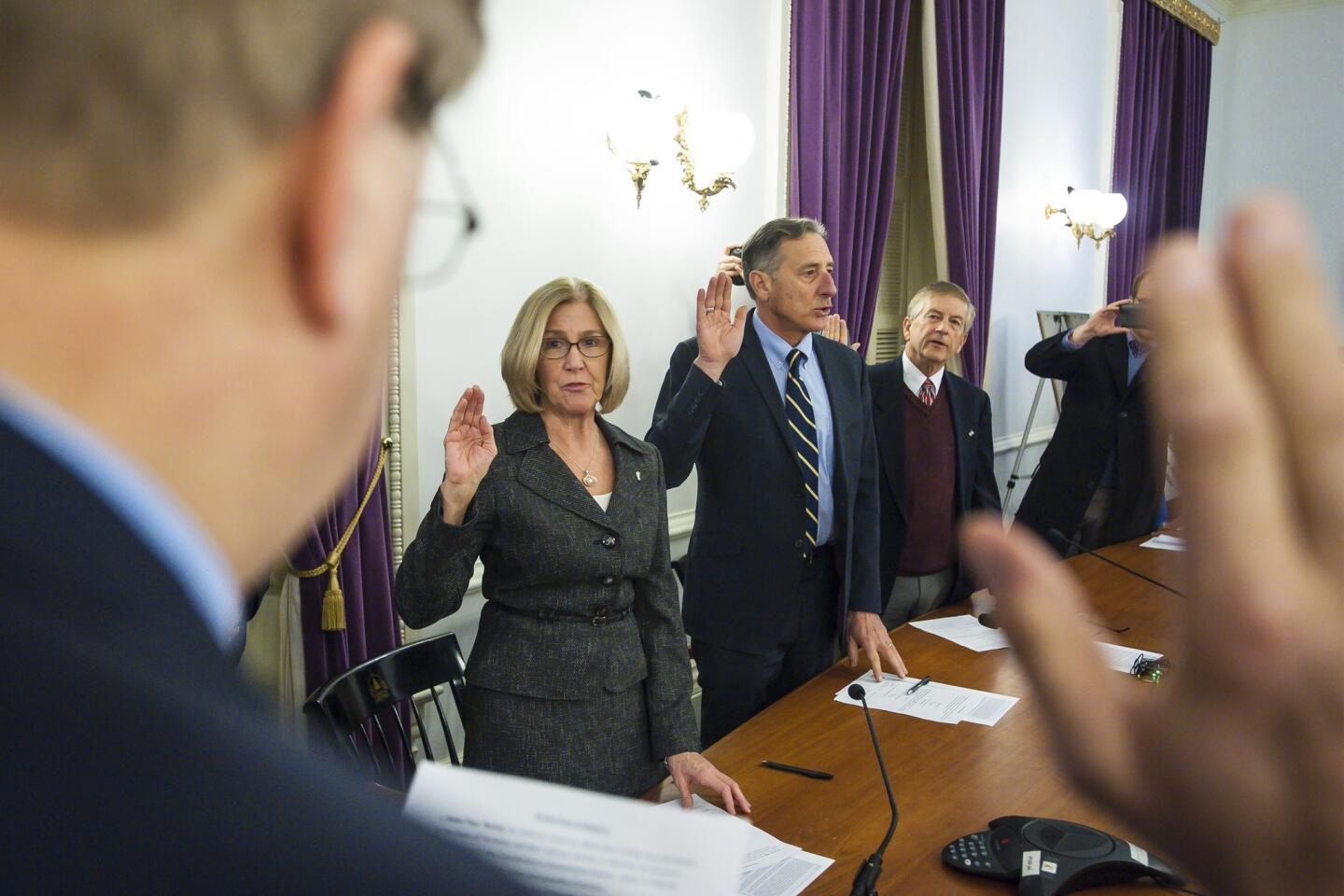
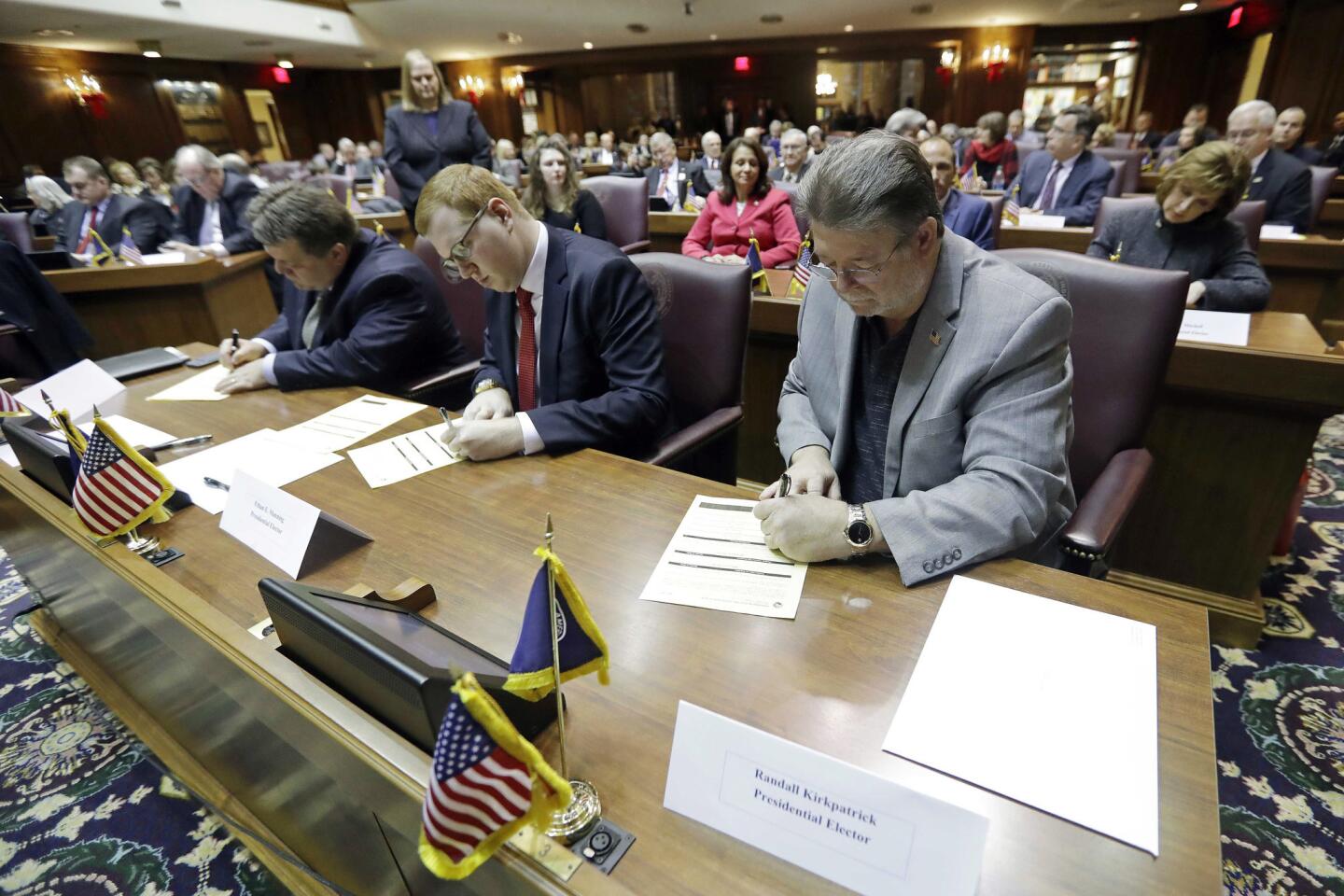
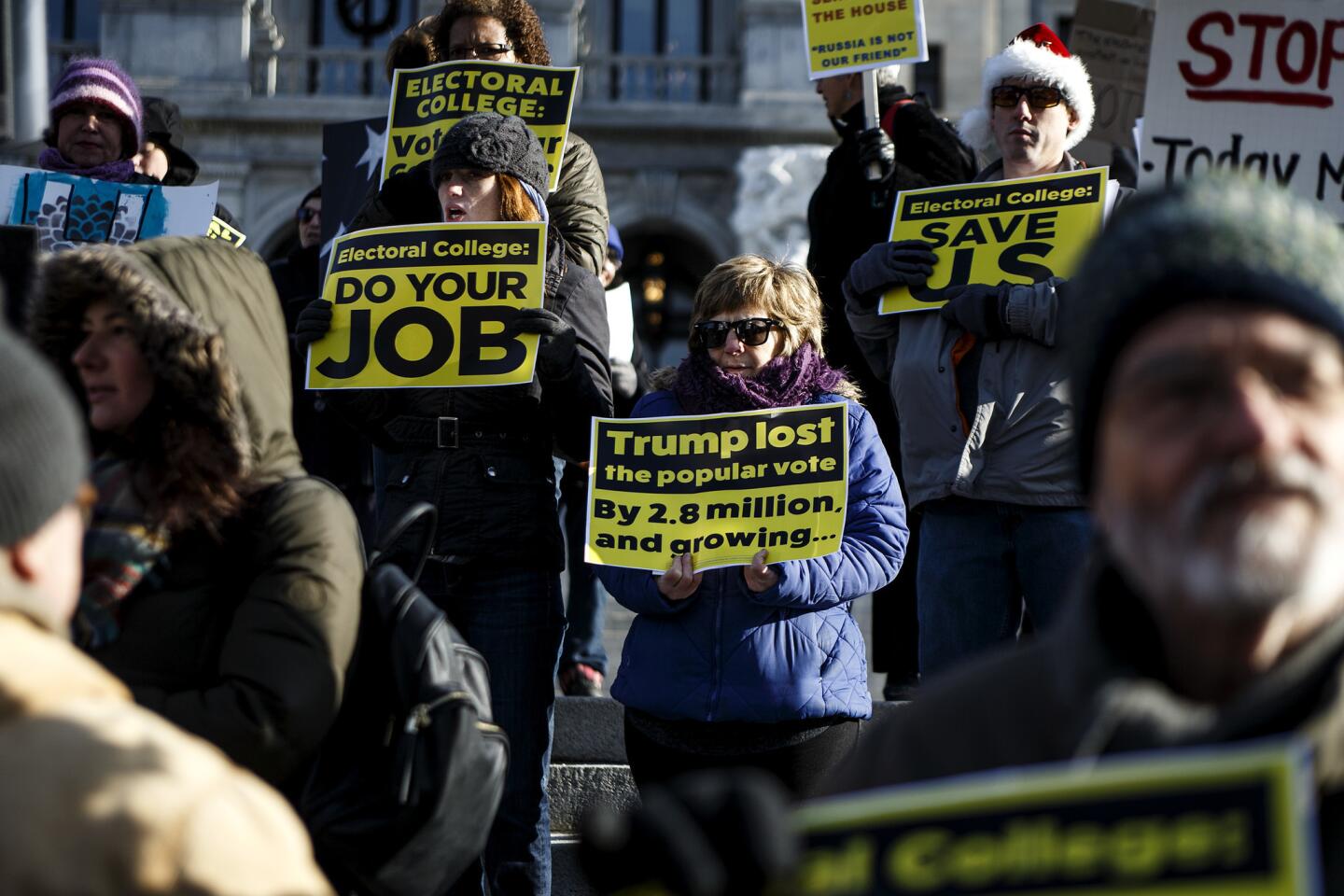
All the times in U.S. history that members of the electoral college voted their own way
They had been lobbied for weeks to abandon Republican presidential nominee Donald Trump. But ultimately, only two members of the electoral college did so, while five members deserted Democratic nominee Hillary Clinton.
It was the largest number of individual defections by electors in a U.S. presidential election — but not enough to change the outcome.
For the record:
3:08 p.m. June 2, 2019An earlier version of this article incorrectly reported that Horace Greeley won the 1872 general election. He lost. The article also misidentified Walter B. Jones as Walter E. Jones.
The final tally in Monday’s vote was 304 votes for Trump and 227 votes for Clinton. The two Republican renegades were from Texas, while Clinton lost pledged votes from Hawaii, Maine and Washington.
These seven individuals join a small club of “faithless electors” in American history.
Samuel Miles of Pennsylvania had the distinction of being the first, in 1796. Miles was a Federalist who had promised to vote for the Federalist candidate, John Adams, but instead cast his vote for Democratic-Republican candidate Thomas Jefferson.
There had been a total of 157 faithless electors until Monday, according to FairVote.org, a nonprofit that advocates for national popular-vote elections for president.
Read more on the transition to Trump »
Several of them broke with the electorate less out of rebellion than for practical reasons. Throughout the years, 71 electors changed their votes because the candidate their state chose died before the electoral college could convene. In 1872, for example, Horace Greeley, the nominee of both the Democratic and Liberal Republican parties, lost the general election and died 24 days later. Sixty-three of the 66 Democratic electors refused to vote for a deceased candidate.
In the 1808 election, which set the previous record for individual defections, six New York electors from the Democratic-Republican party refused to vote for James Madison and voted instead for the party’s vice presidential candidate, George Clinton.
The Constitution does not specifically require electors to cast their votes according to the popular vote in their states, but the laws of 29 states and the District of Columbia bind electors to do so. Some require pledges or threaten fines or criminal action, according to a summary of state laws by the National Assn. of Secretaries of State.
No elector has ever been prosecuted for not voting as pledged.
Since 1900, there have been only 16 faithless electors who defected for individual reasons, including the seven from Monday. Here’s a rundown of who those 16 are and why they voted the way they did:
1948
Preston Parks of Tennessee was chosen as an elector for the Democratic Party, which was pledged to incumbent Harry S. Truman. Before the election, some Democrats opposed to Truman’s support of civil rights and racial integration split off and formed the States’ Rights Democratic Party, also known as the Dixiecrats. Parks actively campaigned for Dixiecrat candidate Strom Thurmond and said in advance of the election that he would not vote for Truman under any circumstances, instead voting for Thurmond.
1956
W.F. Turner, a Democratic elector from Alabama, voted for a local circuit judge, Walter B. Jones, for president instead of the Democratic nominee, Adlai Stevenson. Jones, an avowed white supremacist who in 1960 presided over New York Times Co. vs. Sullivan, which later became a landmark Supreme Court case that defined the standard for journalistic libel, was not on the popular ballot. Fellow electors at the time told Turner he was under an “obligation” to vote for Stevenson because the electors had signed a party loyalty oath. Turner replied: “I have fulfilled my obligations to the people of Alabama. I’m talking about the white people.”
1960
Henry D. Irwin, a Republican from Oklahoma, telegraphed all of his fellow Republican electors in the country asking if they would consider supporting a Barry Goldwater-Harry Byrd ticket over Richard Nixon-Henry Cabot Lodge. Irwin received approximately 40 replies, some favorable, but when it came time to cast their votes, Irwin was the only one who defected. According to an account in the book “Why the Electoral College is Bad for America,” by George C. Edwards III, Irwin told the Senate Judiciary Committee in a subsequent hearing about possibly changing the presidential election procedures that he had worked to get electors to abandon John F. Kennedy and Nixon in favor of a strongly conservative candidate. He said he voted the way he did because he “feared the immediate future of our government under the control of the socialist-labor leadership.”
1968
Lloyd Bailey, a Republican from North Carolina, voted for George Wallace of the American Independence Party over Nixon, the Republican candidate. Bailey was a member of the ultraconservative John Birch Society and, according to Edwards’ book, disliked what he considered to be Nixon’s “leftist” appointments of Henry Kissinger and Daniel Patrick Moynihan to advisory positions, as well as his request to Chief Justice Earl Warren to remain on for an additional six months.
1972
Roger MacBride, a Republican elector from Virginia, deserted Nixon to vote for the candidate of the nascent Libertarian Party, John Hospers, a philosophy professor at USC. MacBride was a political disciple of Rose Lane, according to his obituary in the New York Times. Lane was the daughter of author Laura Ingalls Wilder and an adherent to Ayn Rand’s philosophy of objectivism. After Lane died, MacBride became the guardian of the “Little House on the Prairie” series and produced a television version of it. He went on to become the Libertarian presidential candidate in 1976, but received no electoral college votes.
1976
Mike Padden, a Republican from Washington state, cast his vote for Ronald Reagan (who had lost in the Republican primary) over Gerald Ford, having decided that Ford was not definitively clear in his opposition to abortion. Edwards notes in his book that the 1976 election between Ford and Jimmy Carter was exceptionally close, and had Ford garnered slightly more support, Padden’s faithless vote would have essentially resulted in a tie, throwing the election to the House of Representatives.
1988
Democratic elector Margarette Leach, a nurse and former member of the West Virginia Legislature, voted for vice presidential nominee Lloyd Bentsen as president and presidential nominee Michael Dukakis as vice president. “I wanted to make a statement about the electoral college,” Leach told the New York Times. “We’ve outgrown it. And I wanted to point up what I perceive as a weakness in the system — that 270 people can get together in this country and elect a president, whether he’s on the ballot or not.”
2000
Barbara Lett-Simmons, a Democratic elector from the District of Columbia, left her ballot blank to protest what she called the district’s “colonial status,” or its lack of congressional representation. Lett-Simmons later said she would have voted for Democratic nominee Al Gore if she thought he had a chance of winning. The presidential election that year, between incumbent Vice President Gore and Texas Gov. George W. Bush, was the closest in U.S. history, with 537 votes separating the two candidates in the deciding state of Florida. The narrow margin required a recount and ultimately necessitated a Supreme Court decision. In the end, Bush received 271 electoral votes and Gore 266.
2004
One Minnesota elector voted for vice presidential candidate John Edwards (actually spelled “Ewards” on the ballot) instead of presidential candidate John F. Kerry. That elector also voted for Edwards for vice president. It is not known who it was, since none of the state’s 10 electors identified himself or herself as having cast a protest vote or having made a mistake.
2016
Christopher Suprun, a paramedic and former firefighter who was one of the first responders on Sept. 11, wrote in a New York Times op-ed in the run-up to the electoral college vote that Trump is “someone who shows daily he is not qualified for the office.” Suprun said he had a legal right and constitutional duty to vote his conscience and planned to do so. On Monday, he cast his vote for Ohio Gov. John Kasich.
Another Republican elector from Texas, William Greene, cast his vote for former Texas Rep. Ron Paul, according to the Austin American-Statesman.
(A third Texan, Art Sisneros, had also opposed Trump and resigned from the electoral college ahead of the vote. He was replaced by an alternate.)
In Washington, where voting for a person not nominated by the party carries a $1,000 fine, four electors defected from Clinton, who won the state’s popular vote.
Esther John, who voted for former Secretary of State Colin Powell, told local media she did so “in the hopes that Democrats and Republicans could reconcile.”
Peter B. Chiafolo, a co-founder of the group Hamilton Electors, which seeks to change the electoral process, also voted for Powell. So did Levi Guerra, who, together with Powell, had previously attempted to challenge Washington’s faithless elector law in court.
Robert Satiacum, an environmental activist, voted for Faith Spotted Eagle, a Yankton Sioux elder who has protested against the Keystone XL and Dakota Access pipelines.
In Hawaii, where Clinton won 62% of the vote, elector David Mulinix voted for Vermont Sen. Bernie Sanders because he thought Sanders was the “most qualified” candidate.
Twitter: @AgrawalNina
ALSO:
Trump expected to pick retired Marine Gen. John Kelly to lead Homeland Security Department
Trump names climate change skeptic and oil industry ally to lead the EPA
UPDATES:
Dec. 20, 1:30 p.m.: This article was updated to reflect the results of the Dec. 19 votes in the electoral college.
This article was originally published Dec. 8 at 2:30 a.m.
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.