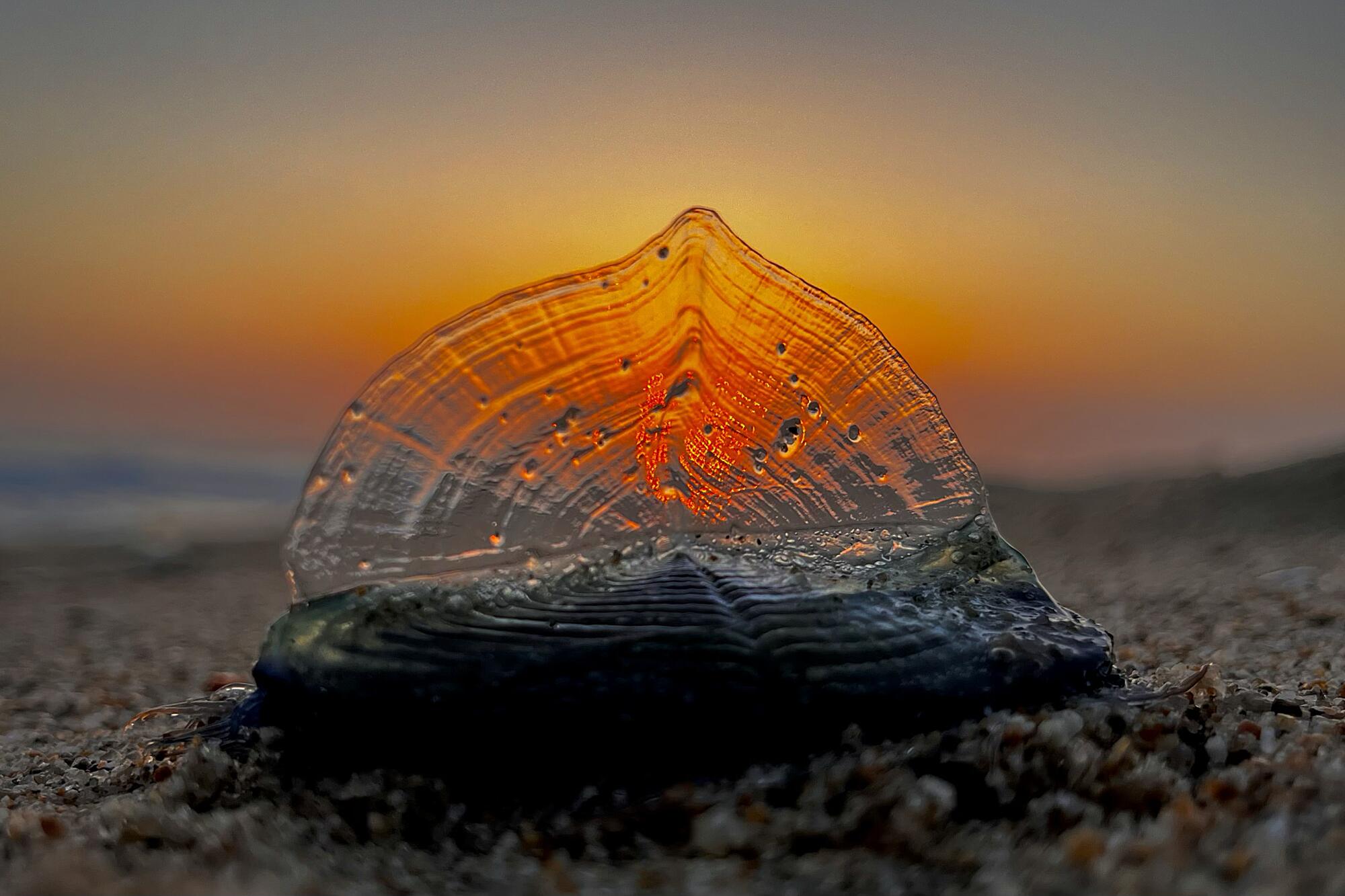
The corpses are washing up by the thousands on Southern California’s beaches: a transparent ringed oval like a giant thumbprint 2 to 3 inches long, with a sail-like fin running diagonally down the length of the body.
Those only recently stranded from the sea still have their rich, cobalt-blue color, a pigment that provides both camouflage and protection from the sun’s UV rays during their life on the open ocean.
Aggressive and impactful reporting on climate change, the environment, health and science.
These intriguing creatures are Velella velella, known also as by-the-wind sailors or, in marine biology circles, “the zooplankton so nice they named it twice,” said Anya Stajner, a biological oceanography PhD student at UC San Diego’s Scripps Institution of Oceanography.
A jellyfish relative that spends the vast majority of its life on the surface of the open sea, velella move at the mercy of the wind, drifting over the ocean with no means of locomotion other than the sails atop their bodies. They tend to wash up on the U.S. West Coast in the spring, when wind conditions beach them onshore.
Springtime velella sightings documented on community science platforms like iNaturalist spiked both this year and last, though scientists say it’s too early to know if this indicates a rise in the animal’s actual numbers.
Velella are an elusive species whose vast habitat and unusual life cycle make them difficult to study. Though they were documented for the first time in 1758, we still don’t know exactly what their range is or how long they live.
These beaching events confront us with a little-understood but essential facet of marine ecology — and may become more common as the oceans warm.
“Zooplankton” — the tiny creatures at the base of the marine food chain — “are sort of this invisible group of animals in the ocean,” Stajner said. “Nobody really knows anything about them. No one really cares about them. But then during these mass Velella velella strandings, all of a sudden there’s this link to this hidden part of the ocean that most of us don’t get to experience.”
What looks like an individual Velella velella is actually a colony of teeny multicellular animals, or zooids, each with their own function, that come together to make a single organism. They’re carnivorous creatures that use stinging tentacles hanging below the surface to catch prey such as copepods, fish eggs, larval fish and smaller plankton.
Unlike their fellow hydrozoa, the Portuguese man o’ war, the toxin in their tentacles isn’t strong enough to injure humans. Nevertheless, “I wouldn’t encourage anyone to touch their mouth or their eyes after they pick one up on the beach,” said Nate Jaros, senior director of fishes and invertebrates at the Aquarium of the Pacific in Long Beach.
Velella that end their lives on California beaches typically have sails that run diagonally from left to right along the length of their bodies, an orientation that catches the onshore winds heading in this direction. As the organism’s carcass dries in the sun and the soft tissues decay, the blue color disappears, leaving the transparent chitinous float behind.
“The wind really just brings them to our doorstep in the right conditions,” Jaros said. “But they’re designed as open ocean animals. They’re not designed to interact with the shoreline, which is usually why they meet their demise when they come into contact with the shore.”
1
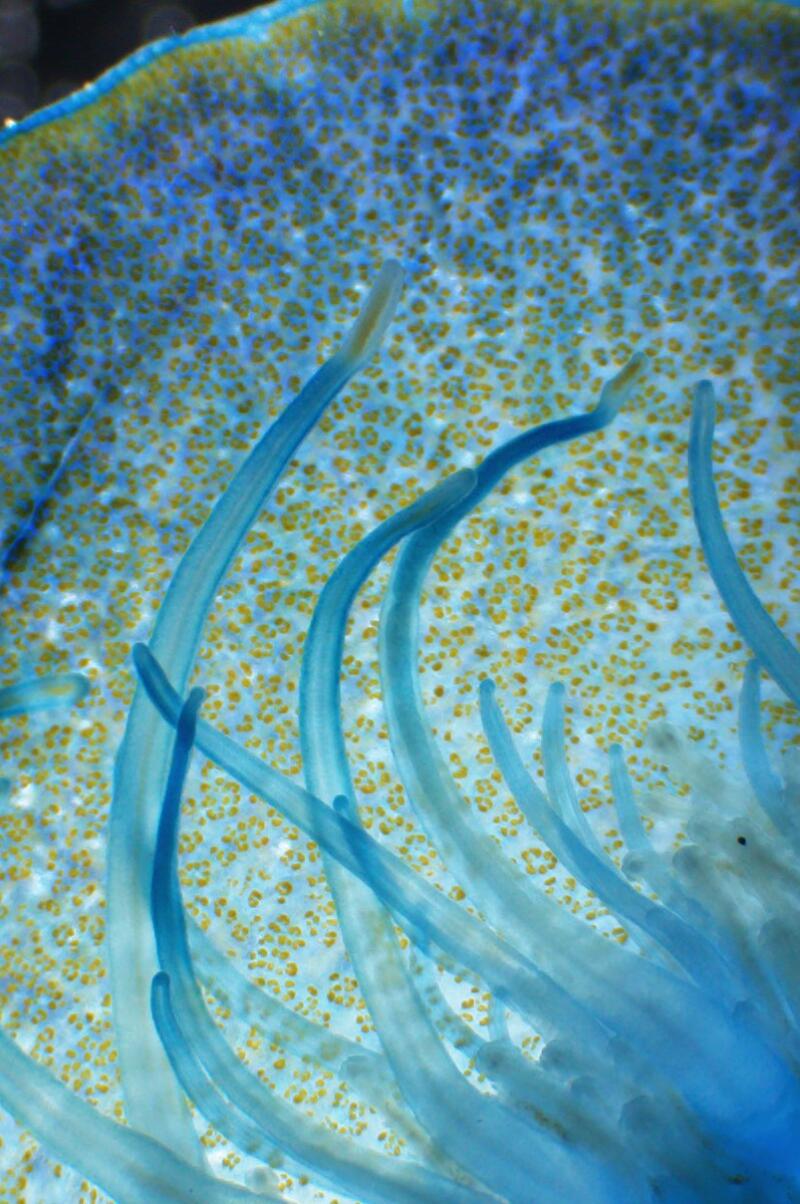

2
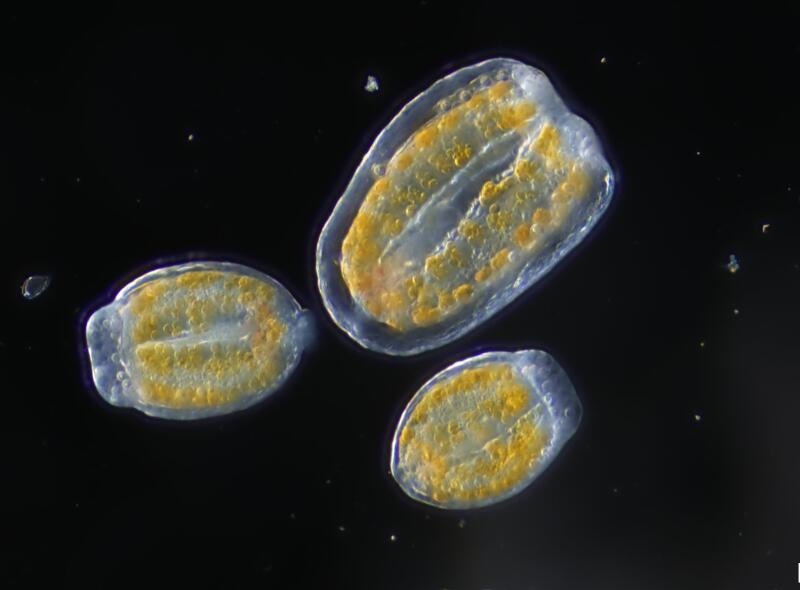
3
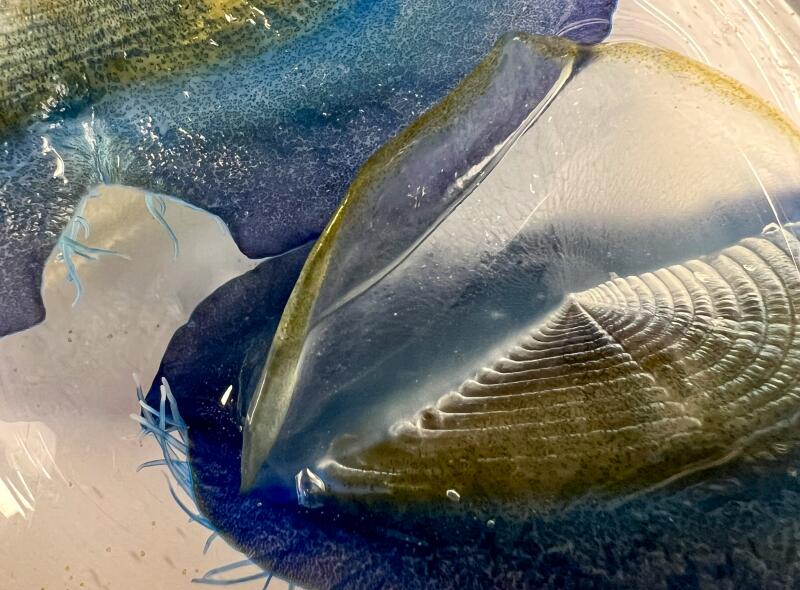

1. Anya Stajner put Velella velella under a microscope. 2. Magnified, you can see more than blue in the organism. “That green and brown coloration comes from their algae symbionts,” Stajner said. 3. Notice the tentacles too. (Anya Stajner)
Velella show up en masse when two key factors coincide, Stajner said: an upwelling of food-rich, colder water from deeper in the ocean, followed by shoreward winds and currents that direct the colonies to beaches.
A 2021 paper from researchers at the University of Washington found a third variable that appears to correlate with more velella sightings: unusually high sea surface temperatures.
After looking at data over a 20-year period, the researchers found that warmer-than-average winter sea surface temperatures followed by onshore winds tended to correlate with higher numbers of velella strandings the following spring, from Washington to Northern California.
“The spring transition toward slightly more onshore winds happens every year, but the warmer winter conditions are episodic,” said co-author Julia K. Parrish, a University of Washington biologist who runs the Coastal Observation and Seabird Survey Team community science project.
Given that sea surface temperatures have been consistently above the historical average every day since March 2023, the current velella bloom is consistent with those findings.
Previous research has found that gelatinous zooplankton like velella and their fellow jellyfish thrive in warmer waters, portending an era some scientists have referred to as the “rise of slime.”
Other winners of a slimy new epoch would be ocean sunfish, a giant bony fish whose individuals can clock in at more than 2,000 pounds and consume jellyfish — and velella — in mass quantities. Ocean sunfish sightings tend to rise when velella observations do, Jaros said.
“The ocean sunfish will actually kind of put their heads out of the water as they eat these. It resembles Pac-Man eating pellets,” he said. (KTLA-TV published a picture of just that this week.)
Though velella blooms are ephemeral, we don’t yet know how long any individual colony lives. The blue seafaring colonies are themselves asexual, though they bud off tiny transparent medusas that are thought to go to the deep sea and reproduce sexually there, Stajner said. The fertilized egg then evolves into a float that returns to the surface and forms another colony.
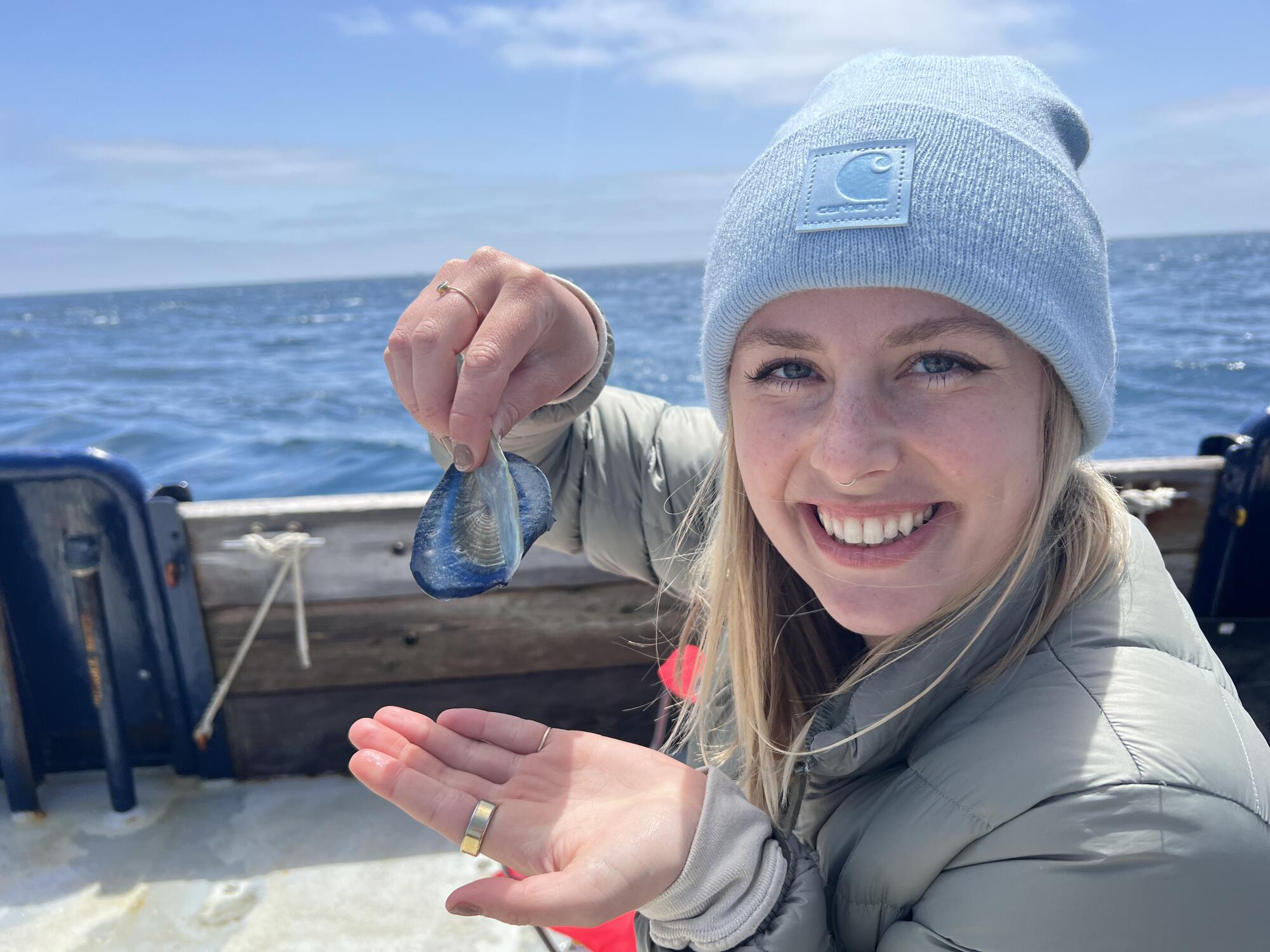

“I was able to actually collect some of those medusae last year during the bloom, but rearing gelatinous organisms is pretty difficult,” Stajner said. The organisms died in the lab.
Stajner left May 1 on an eight-day expedition to sample velella at multiple points along the Santa Lucia Bank and Escarpment in the Channel Islands, with the goal of getting “a better idea of their role in the local ecosystem and trying to understand what these big blooms mean,” she said.
T. rex intelligence was likely much closer to that of modern-day crocodiles than primates — a perfectly respectable amount of smarts for a therapod.










